Assessing indoor radon levels using a Scale Model Room (SMR)
A Scale Model Room (SMR)(62 cm length, 50 cm width, 35 cm height) was constructed using bricks of a lithoid ignimbrite (Tufo Rosso a Scorie Nere) and a
concrete without Pozzolanic ash. This stone is one of the building material mostly used in Caprarola. The model room was placed on a wood floor, closed with a plastic roof, and connected with RAD7 monitors for experiments.
Several experiments were conducted; a first test was carried out to determine experimental 222Rn equilibrium activities in the model room, not covered
with plaster or other coating material. A second test was performed after sealing the external faces of the room with a transparent film commercially used to
conserve foods. In both tests the atmospheric conditions of the laboratory (temperature, relative humidity and atmospheric pressure) were similar.
The results of these experiments are shown in Figure 1.
In the first test the radon concentration reaches the equilibrium value (770 Bq/m3) in about 10 hours. In the second test, with the walls externally covered by
a waterproof film, radon concentration reaches the equilibrium (10600 Bq/m3) in a time of about 76 hours. The second experiment (i.e., external walls
covered by a waterproof film) shows how an external cover strongly limit the indoor air dilution through the very porous ignimbrite (43%), exponentially
increasing the accumulation of radon within the SMR. Other tests about the correlation among indoor radon and temperature, relative humidity and
pressure gradients of external environment are in progress.
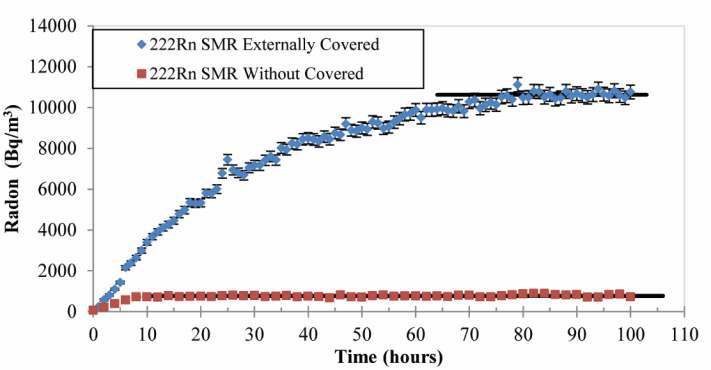
covered by a waterproof film. In red: radon concentrations inside the SMR with the walls “free to breathe” (without externally covered)